
For Physicians
*SiFix is available as an in-office procedure for its Intra-Articular implant. Reach out to learn more information.
What We Offer
-
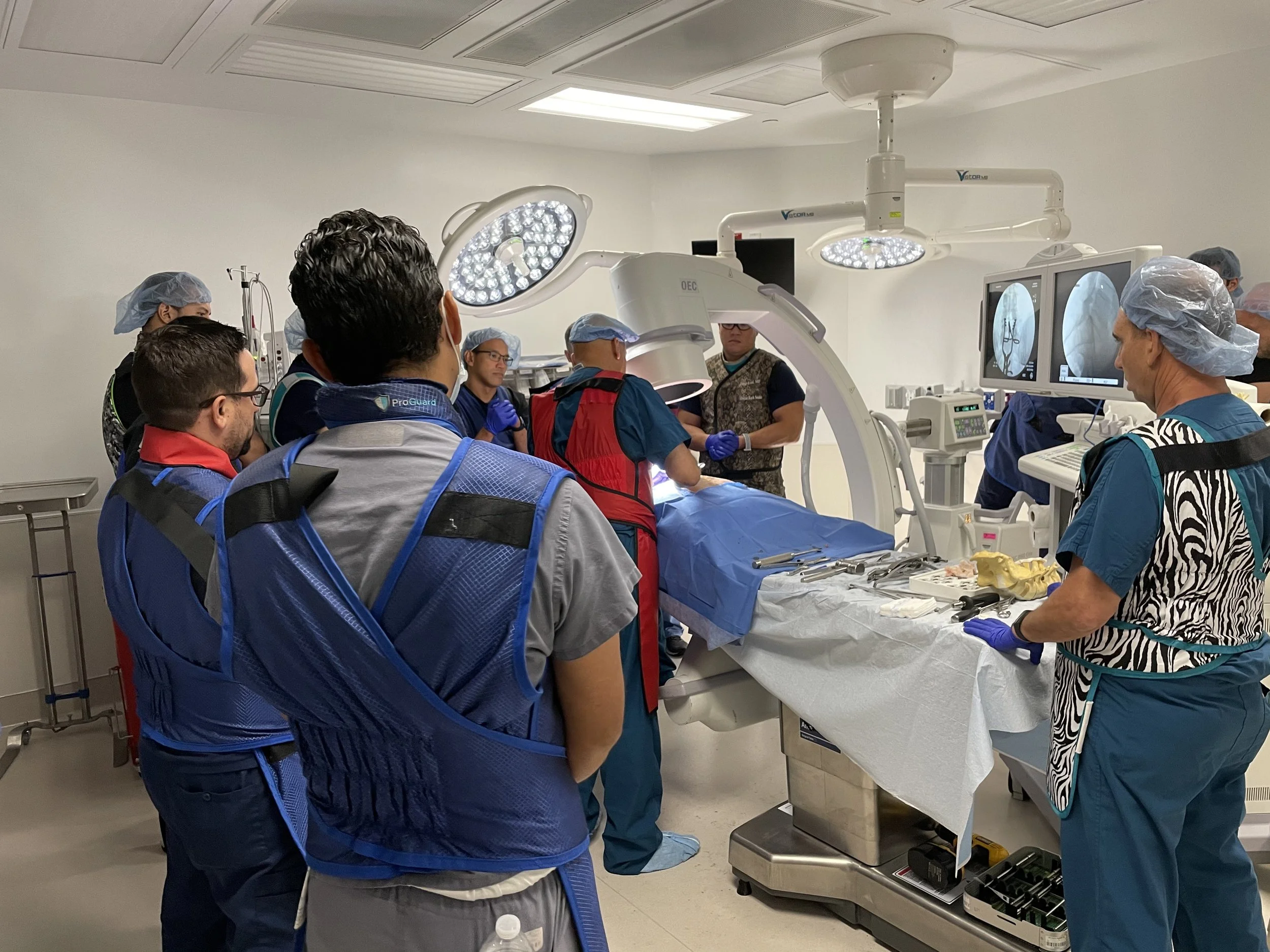
Cadaveric Training
-

In-Office Synthetic Training
-

Online Webinars for Both Doctors and Staff
-

Prior Authorization Software
Sacroiliac Joint
The SiFix Systems Has Several Major Benefits Compared to Traditional Si Joint Fusion Systems.
Minimally Invasive system with typically less than 5ml of blood loss during the whole procedure
Faster recovery time than traditional systems
Multiple implant options for coding
Posterior Approaches that are safely away from blood vessels and nerves
Lateral Approaches that offer self drilling and self taping implants
“Up to 30% of low back pain may be from the Si Joint” (1)
“75% of lumbar fusion leads to Si Joint pain” (2)
(1)Weksler N, Velan GJ, Semionov M, Gurevitch B, Klein M, Rozentsveig V, Rudich T. The role of sacroiliac joint dysfunction in the genesis of low back pain: the obvious is not always right. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2007 Dec;127(10):885-8. doi: 10.1007/s00402-007-0420-x. Epub 2007 Sep 8. PMID: 17828413.
(2)Ha KY, Lee JS, Kim KW. Degeneration of sacroiliac joint after instrumented lumbar or lumbosacral fusion: a prospective cohort study over five-year follow-up. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008 May 15;33(11):1192-8. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e318170fd35. PMID: 18469692.
Patient Identification-Sacroiliac
*Not all symptoms may be present and can be isolated to only one indicator. Other common pain areas include, but are not limited to, the hip, groin, and buttocks.
Lower Back Pain
The most common symptom is pain in the lower back, typically on one side or both sides of the spine. The pain may be described as a dull ache, a sharp or stabbing pain, or a constant discomfort.
Pain When Lying on One Side
Individuals with SI joint pain may find it uncomfortable to lie on one side, particularly on the affected side.
Leg Pain
Pain can radiate down one or both legs, often along the sciatic nerve distribution. This can lead to symptoms similar to sciatica, such as leg pain, numbness, tingling, or weakness.
Stiffness
Some people with sacroiliac joint dysfunction may experience stiffness in the lower back, pelvis, or hips, especially in the morning or after periods of inactivity.
Pain with Activity
Sacroiliac joint pain is often aggravated by specific activities or movements, such as walking, climbing stairs, standing for extended periods, or transitioning from sitting to standing.
Pain During Physical Activities
Activities that involve twisting or bending at the waist, lifting heavy objects, or bearing weight unevenly on the pelvis can trigger or exacerbate SI joint pain.
Facet Joint vs Lumbar Pain
Facet
-
Location
Localized to low back, often off-center, may radiate to buttocks or upper thigh.
Pain Onset
Often insidious, worse with age or arthritis
Pain Type
Dull, aching, worse with extension or twisting
Referred Pain Pattern
Referred pain in a non-dermatomal pattern (e.g. buttock, upper thigh)
Relieved By
Flexion (bending forward), heat, rest
-
Straight Leg Raise (SLR)
Usually negative
Pain with Flexion (bending forward)
Often better
Pain with Extension (leaning back)
Worse
Palpation
Localized tenderness over facet joints (1-2 cm lateral to midline)
-
MRI
Joint hypertrophy, sclerosis, narrowing of joint space
X-Ray
May show facet arthritis but not soft disc pathology
CT
Best for bone details (e.g., facet joint arthropathy)
-
Facet Joint Medial Branch Blocks
Temporary relief = facet pain
Lumbar
-
Location
Deep, central low back, possibly radiating to the buttocks or legs (esp. if nerve root involved)
Pain Onset
Can be acute (injury) or chronic
Pain Type
Aching or sharp, may be worse with sitting or flexion
Referred Pain Pattern
May follow a dermatomal pattern if nerve root involved
Relieved By
Lying flat, walking short distances
-
Straight Leg Raise (SLR)
Often positive (esp. with radiculopathy)
Pain with Flexion (bending forward)
Worse
Pain with Extension (leaning back)
Usually better
Palpation
May elicit diffuse tenderness
-
MRI
Disc bulges, herniation, Modic changes, annular tears
X-Ray
May show narrowing of disc space
CT
Confirm bone details such as stenosis or narrowing of disc or foramen
-
Reproduces discogenic pain when injecting contrast into the disc (rarely used)






